In project management, tracking project success is essential. Misalignment between business and project objectives causes over 44% of projects to fail. How can you bridge this gap? How can you ensure your project aligns with your business goals and delivers the desired project value? If you rely on data analytics for informed decision-making, allocating time and effort to measure project success is crucial.
Effective project success tracking ensures that your projects meet their goals and add measurable value to your organization. Project success tracking involves understanding the expected value, measuring it, using the necessary project management tools and solutions, and communicating the value to senior leadership. Unfortunately, many organizations overlook consistent metrics tracking and real-time insights, which can be easily achieved with predictive project management solutions.
As project management trends evolve, they pave the way for enhanced productivity among team members. Project managers are adopting innovative methods to motivate their teams and ensure the successful execution of projects. The advent of new technologies and economic shifts are revolutionizing the tasks within organizations, offering a fresh perspective on time and effort estimation and management. The current landscape, influenced by technological, social, and market factors, is poised to reshape the execution of project management.
So, the pressing question emerges, “What are the essential project success measurement metrics that demand monitoring?” This article highlights the significance of tracking project success measurement for performance, decoding metrics, and harnessing actionable insights to steer decision-making and boost project performance. The article further explores TrueProject, a KPI-based predictive project management solution. It measures and tracks your project KPIs against real-time data and regularly benchmarks them against governance guidelines, ensuring your project meets all the standards.
Definition Of Project Success Management Metrics
 Project success measurement metrics provide a quantifiable view of performance, aiding in tracking scheduling, budgeting, task management, and quality control. They are essential for assessing success, setting benchmarks, enabling performance evaluation, supporting data-driven decisions, fostering transparency, and identifying improvements. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), project managers can align team efforts with strategic goals and enhance project outcomes.
Project success measurement metrics provide a quantifiable view of performance, aiding in tracking scheduling, budgeting, task management, and quality control. They are essential for assessing success, setting benchmarks, enabling performance evaluation, supporting data-driven decisions, fostering transparency, and identifying improvements. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), project managers can align team efforts with strategic goals and enhance project outcomes.
Project success measurement metrics are quantifiable indicators used to gauge the organization's progress based on data. These typically encompass:
- Cost efficiency, measured by comparing the actual expenditure with the initial budget.
- Progress of the project, evaluated by the percentage of work completed, milestones achieved, or the time invested.
- Financial gain, such as the return on investment.
- Quality indicators are determined by the degree to which the final product meets customer expectations.
- Stakeholder contentment, assessed through customer surveys or an employee satisfaction index.
These performance metrics are crucial for ensuring the project aligns with organizational goals and delivers desired outcomes.
Why Is Project Success Measurement Important?
Understanding the project success measurement offers benefits beyond merely knowing the project’s status or completion deadline. Here are some ways in which tracking and analyzing key metrics can aid in the current project lifecycle and future projects as well:
- Enhance Quality and Performance – Performance metrics guide you to make changes that boost your project’s success. Setting success indicators and measuring baselines allows you to monitor the project’s progress effectively.
- Understand Industry Trends - A data-driven approach helps you compare your company’s performance with others in your industry. For instance, your revenue might seem to be slowing down, but you might outperform your competitors in the current market.
- Track Costs and Conserve Resources - Financial metrics ensure smooth business operations and prevent budget overruns. Improving a cost performance index can also enhance profit margins and business growth.
- Mitigate Risk and Enhance Safety - Project metrics give insights into your business operations, allowing you to address minor shifts before they become major issues.
Project success measurement is vital as it helps improve processes, understand industry trends, conserve resources, and reduce risks.
The following graphic compiles project management statistics and facts from various reputable sources.

How Do You Choose the Right Project Success Measurement Criteria
Selecting the appropriate project management solution is a crucial aspect of project execution. Numerous project success measurement metrics are available, but not all may be relevant or beneficial to your organization. Here’s how you can choose the right ones:
- Project Scope, Size, and Complexity - Basic metrics like cost efficiency might be sufficient for simple projects with a small team. However, for larger, more complex projects involving multiple teams, more comprehensive metrics may be needed to capture and monitor the project’s progress accurately.
- Project Importance - The significance of a project within the company’s financial framework can influence the level of detail in the metrics used. High-priority or recurring projects might require more detailed metrics, while smaller, one-off projects might need less scrutiny.
- Organizational Objectives - Each organization has unique goals and priorities. Some prioritize profit margins, while others balance financial metrics with employee satisfaction scores. Ensuring that the metrics you measure align with these organizational objectives is important.
Selecting and utilizing project success measurement metrics for team success is a strategic process. It involves identifying project goals, defining SMART goals, choosing relevant metrics, and creating a project success measurement plan to enhance outcomes. Here are the key elements to consider while selecting the project success measurement metrics:
- Selecting Project Management Metrics for Team Success:
- Identify specific project goals,
- Define SMART goals aligned with project objectives,
- Choose key metrics related to project goals,
- Develop a plan detailing how and when to measure selected metrics.
- Collecting and Analyzing Project Management Metrics:
- Track performance, resource allocation, budget use, and project progress,
- Establish a process to interpret and analyze data,
- Use data analytics solutions for efficient data organization and visualization,
- Interpreting Project Management Metrics:
- Set performance benchmarks for scope, cost, and time,
- Analyze trends and patterns from performance data,
- Identify areas needing improvement,
- Use metrics to guide decision-making.
- Utilizing Project Management Metrics for Success:
- Monitor task completion, cost variance, and schedule variance,
- Address potential issues promptly through real-time data analysis,
- Regularly assess KPIs to optimize project performance,
- Align projects with organizational objectives.
- Track and Improve Project Performance:
- Customize dashboards to meet project and team requirements,
- Gain a holistic view of project performance,
- Track, measure, and optimize key project milestones and goals,
- Ensure smooth project delivery with capacity planning and resource reports,
- Enhance planning accuracy with time-tracking reports.
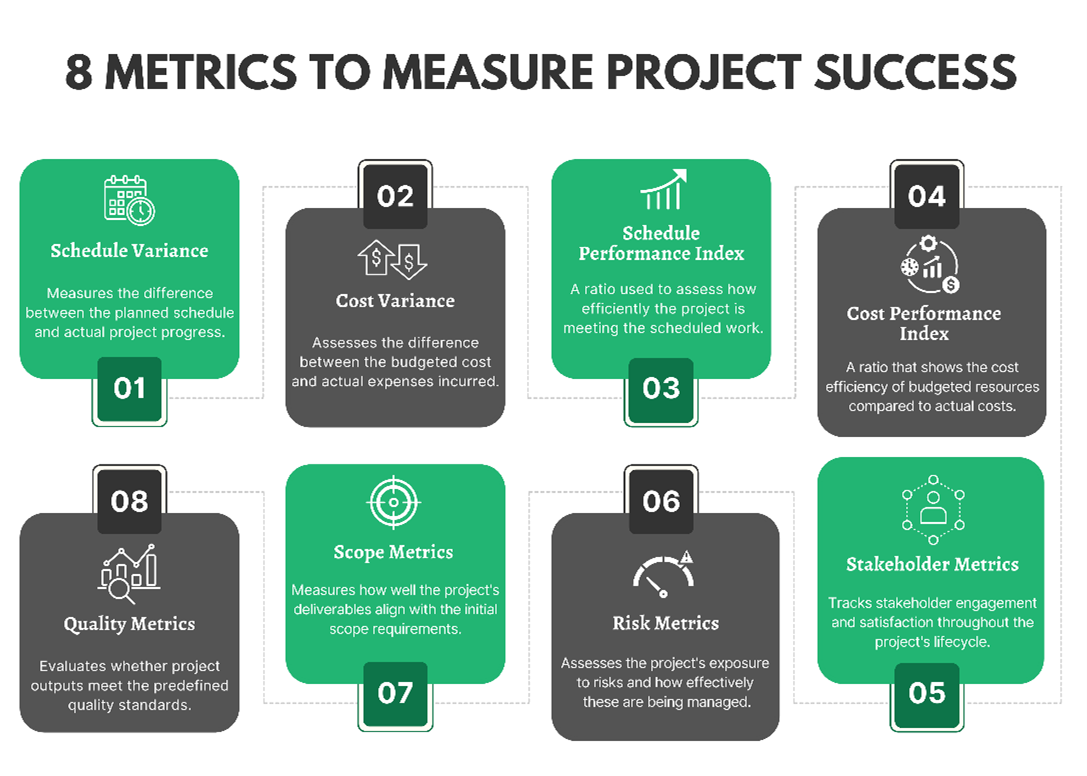
Types of Project Success Measurement
Project success measurement metrics enable a project manager to track progress, identify bottlenecks, analyze data, and optimize performance. Here are some types of metrics that can be effectively used:
- Schedule Metrics - Focuses on timelines, comparing planned versus actual schedules. They include Actual Schedule Performance (ASP), which measures progress against the planned timeline; Schedule Variance (SV), which indicates whether the project is ahead or behind schedule; and Schedule Performance Index (SPI), a measure of efficiency.
- Cost Metrics - Measures the financial aspects of projects. They include Actual Cost Performance (ACP), which measures the total costs incurred for the work performed; Cost Variance (CV), which measures the difference between the budgeted and actual costs; and Cost Performance Index (CPI), which measures cost efficiency.
- Quality Metrics - Helps maintain standards and meet customer expectations. They include Defect Density, which quantifies the number of defects in a deliverable, and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), which measures customer satisfaction with a product or service.
- Scope Metrics - Focuses on the project’s objectives. They include Scope Creep, which quantifies the extent of changes or additions not initially included in the project’s scope.
- Risk Metrics - Assists in proactive risk management. They include Risk Exposure, which quantifies the probability and impact of a risk, and Risk Impact, which assesses the potential effects of identified risks on project outcomes.
Additionally, leveraging predictive project management solutions that seamlessly integrate into project management provides a forward-looking lens, enhancing your ability to anticipate challenges and opportunities. This, in turn, adds a new dimension to project success measurement. By understanding and properly utilizing these various project management metrics, project managers can guide their projects toward successful completion.
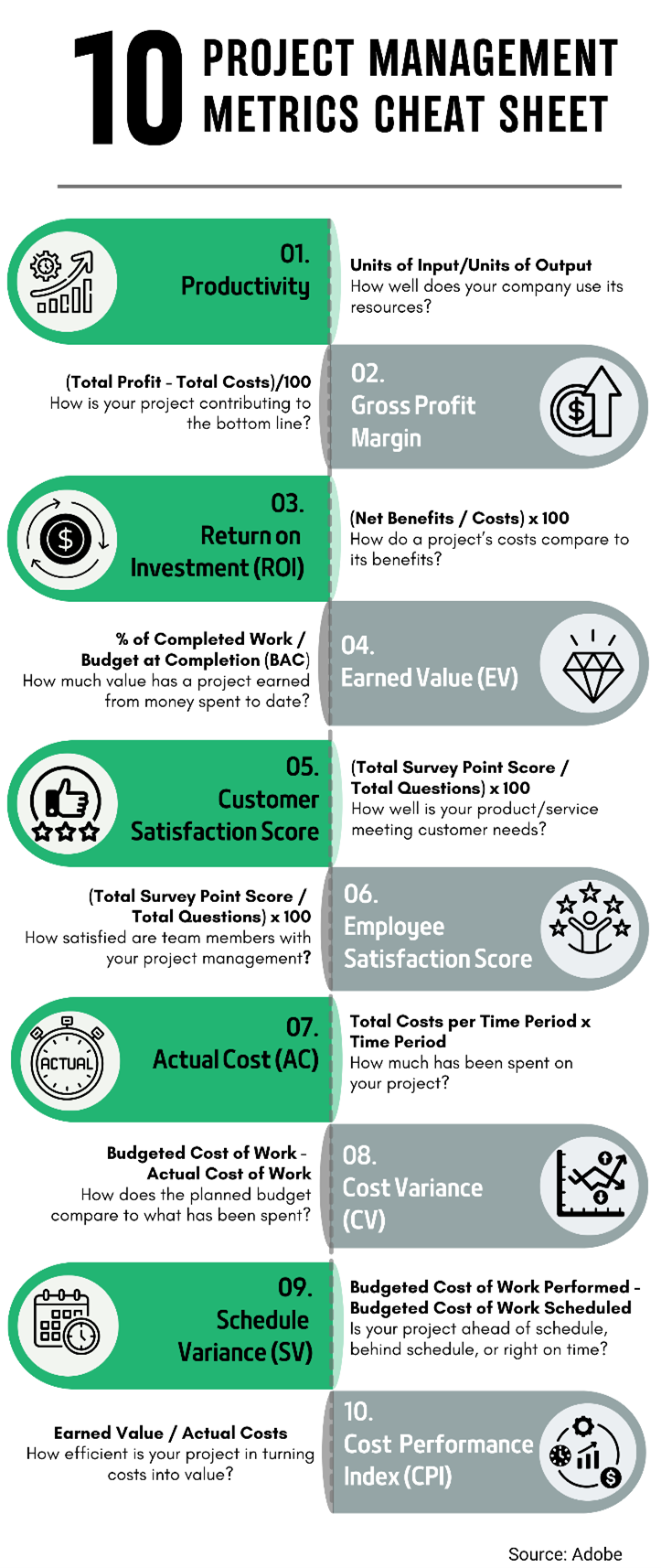
17 Project Success Measurement You Must Track
Understanding key project success measurement metrics is essential for any business aiming for success. This comprehensive list provides metrics across different domains. Each metric serves as a vital indicator to track project success measurement and make strategic decisions:
- User Retention - Indicates user value, optimizes features for advantage and uses low retention for feedback.
- Time To Value - Measures project success and impact, implies efficiency in a shorter time, and aids in resource optimization.
- Client Satisfaction - A key metric for project success measurement and meeting expectations.
- Product-Market Fit - Evaluates customer value, gauges satisfaction, and focuses on exceptional value delivery.
- Business Value - Aligns projects with objectives and provides benefits, including cost savings and improved customer experience.
- Customer Experience - A crucial metric for tech project success that enhances processes and effectiveness.
- User ‘Aha!’ Moments - Showcases project effectiveness and measures user realization of core value.
- ROI (Return on Investment) - Essential for project approval and measures financial impact.
- Net Promoter Score - Indicates user recommendation likelihood and ensures customer support.
- Churn Rate - Measures customer dropout rate and provides retention insights.
- Delivery Timeline - Planned vs. Actual - Compares delivery times and reflects financial target achievement.
- Competitive Advantage - Judges project success by sales impact and potential influence.
- User Feedback - Provides insights for future project improvements.
- User Engagement - Reflects user commitment and indicates marketing strategy success.
- Innovation Adoption Speed - Measures user adoption rate and signifies project execution effectiveness.
- Customer and Employee Happiness - Crucial in a competitive environment and reflects system impact on relationships.
- Customer Acquisition Cost - Measures new customer cost and acknowledges the importance of customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Project management metrics offer crucial insights into a project's performance and are vital to project success. By selecting the right metrics, aligning them with project objectives, and utilizing data analytics effectively, project managers can track progress, identify issues promptly, optimize performance, and ensure alignment with organizational goals. By adopting advanced predictive solutions and project success measurement metrics, organizations can enhance productivity, improve decision-making processes, and increase the likelihood of project success in an evolving project management landscape.
Modern predictive solutions provide insights to for project success measurement and help organizations identify trends, mitigate risks, enhance services, and make real-time informed decisions. Leveraging advanced predictive solutions, like TrueProject, offers more than task management. TrueProject, a KPI-based predictive project management SaaS solution, benchmarks your organization against the project repository, focusing on people and processes. It identifies areas needing attention while there is time to act. As a predictive intelligence solution, TrueProject guides you based on governance and measures project success, ensuring your projects always stay on track. It provides next steps and early warnings to avoid surprises that can become pitfalls for project success. TrueProject is a powerful predictive and prescriptive solution that aids project success measurement and ensures nothing is overlooked, helping you consistently deliver your projects with guaranteed insights for success.

About the Author:
Nisha Antony is an accomplished senior marketing communications specialist at TrueProject and a leader in predictive intelligence. With over 16 years of experience, she has worked as a Senior Analyst at Xchanging, a UK consulting firm, and as an Internal Communications Manager on a major cloud project at TE Connectivity.
She is an insightful storyteller who creates engaging content on AI, machine learning, analytics, governance, project management, cloud platforms, workforce optimization, and leadership.
Endnotes
- Sakshi Sacheti. “Measuring Project Success And Project Performance Indicators.” LinkedIn: Sep 13, 2023. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/measuring-project-success-performance-indicators-sakshi-sacheti/
- Forbes Expert Panel. “17 Metrics For Evaluating The Success Of Tech Projects And Initiatives.” May 24, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/05/24/17-metrics-for-evaluating-the-success-of-tech-projects-and-initiatives/?sh=493a26c7530b
- Mae Angeline. “The 5 Project Success Metrics that Matter.” Runn: Jul 28, 2022. https://www.runn.io/blog/project-success-metrics
- Adobe Communications Team. "Metrics for Project Management: How to Measure & Track Success." Adobe: Mar 18, 2022. https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/metrics





